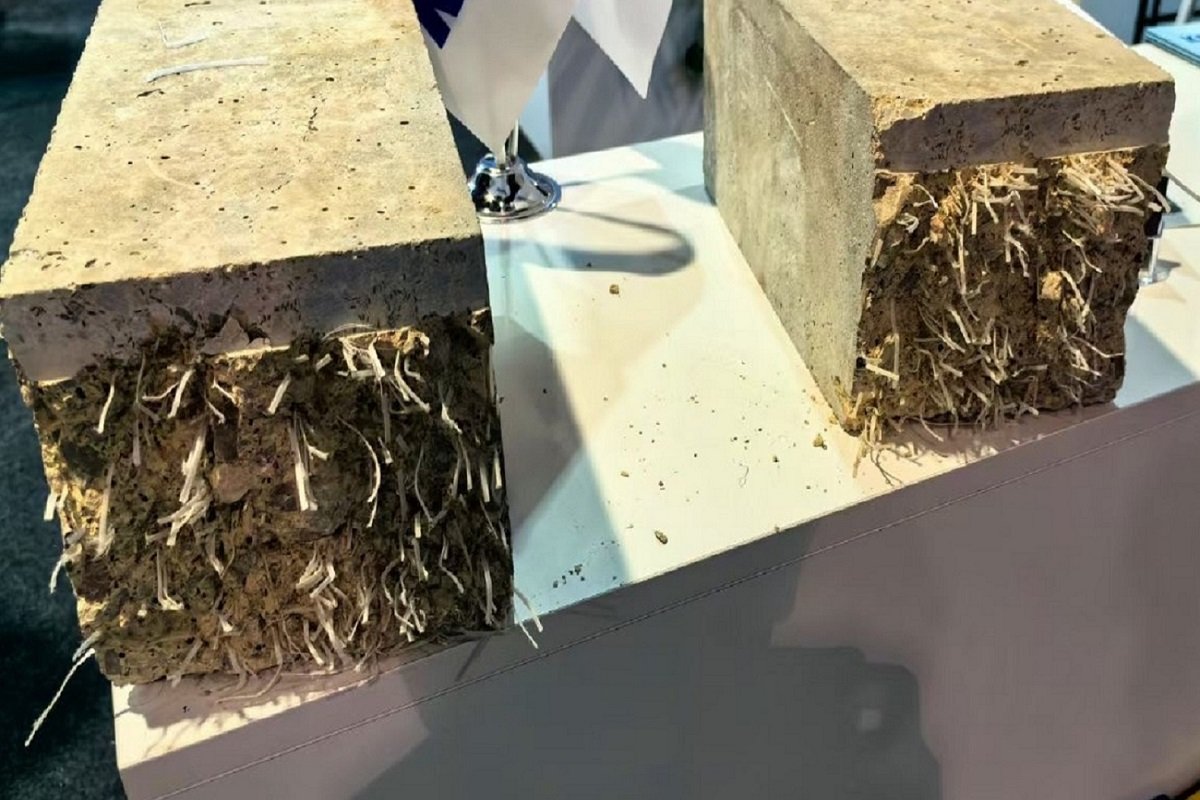
Hello everyone, I’m Director Wang. Now, let’s explore the relationship between synthetic fibers and concrete from the perspective of production manufacturers, focusing on four aspects of synthetic fiber-reinforced concrete.
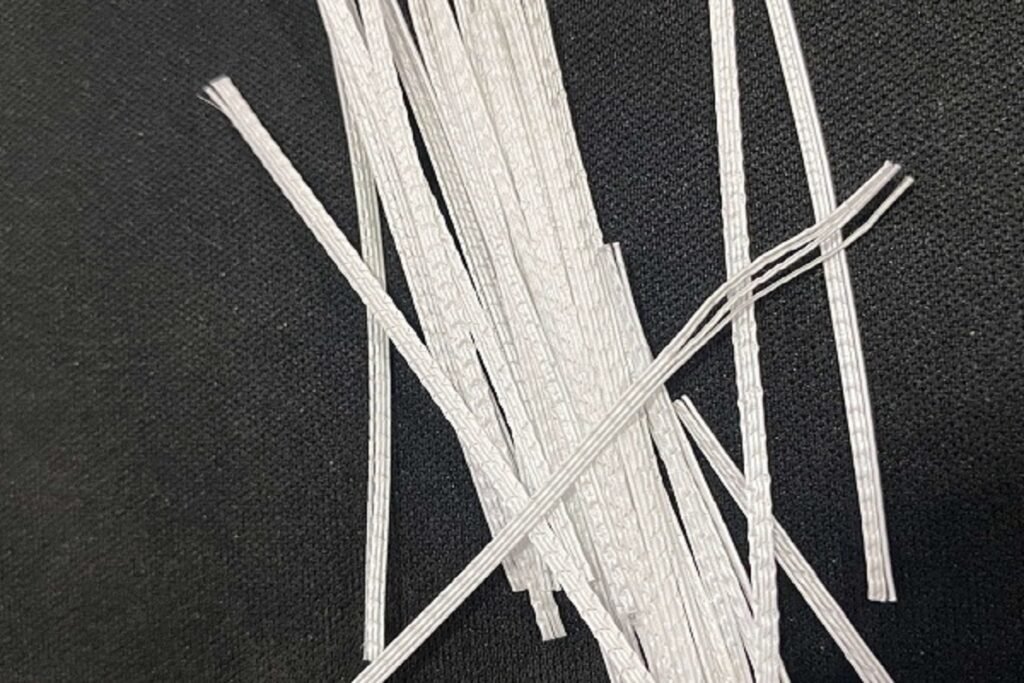

1. What is Synthetic Fiber Reinforced Concrete?
Simply put, concrete with added synthetic fibers is synthetic fiber reinforced concrete. These fibers alter the original basic properties of the concrete, making it more stable, less prone to cracking, and highly durable, which has led to its increasing popularity among builders. Synthetic fiber reinforced concrete is a type of composite material where the properties of the synthetic fibers determine the performance of the final product.
2. What are the Functions of Synthetic Fibers in Concrete?
As a manufacturer, I understand that the performance of synthetic fibers is crucial. Let’s look at the related properties of synthetic fibers and synthetic fiber reinforced concrete from a fundamental perspective.
2.1 Enhancing Impact Resistance:
Impact resistance is one of the crucial properties of concrete. For synthetic fibers, this includes basic performance characteristics such as length, equivalent diameter, tensile strength, and elongation at break. The length and equivalent diameter, or the aspect ratio, directly affect how fibers are distributed and oriented within the concrete. A good aspect ratio allows fibers to distribute more of the concrete’s pre-stress three-dimensionally, enhancing the overall strength and durabili

2.2 Reducing Crack Index:
One major role of the elastic modulus of synthetic fibers is reducing the crack index of concrete. A higher elastic modulus means the fibers can better withstand and distribute stress, thereby inhibiting crack formation.
2.3 Increasing Toughness Index:
Concrete reinforced with synthetic fibers has significantly improved toughness compared to non-reinforced concrete. The higher the performance indicators of synthetic fibers, the better the toughness of the concrete.
Through these basic performance indicators, we can theoretically conclude that synthetic fibers fundamentally improve concrete by reducing its brittleness, enhancing toughness, and increasing impermeability.

3. When Should Synthetic Fibers be Added to Concrete?
Synthetic fibers are suitable for almost all concrete applications. Polypropylene fibers, for instance, are acid, alkali, and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for any concrete engineering project, regardless of the environment. Thus, synthetic fibers should always be considered to address fundamental concrete issues, enhancing performance at any time, place, or project.
4. Types of Synthetic Fibers in Concrete
4.1 Polypropylene Synthetic Fibers:
Polypropylene fibers are the most common and widely used. There are two types: microfibers (also known as monofilament fibers) used mainly in mortars for crack resistance and permeability improvement, and macro fibers used for structural reinforcement due to their stable performance.
4.11 Why are Polypropylene Synthetic Fibers Widely Used?
From a manufacturer’s viewpoint, polypropylene is cost-effective and easy to process. We can fully master the production process and performance. For concrete mixing stations, polypropylene fibers do not affect water ratios and are easy to add due to their light weight, saving labor costs. For material suppliers, these fibers are stable and inexpensive. For construction workers, they prevent cracking, are simple to apply, and have low maintenance costs, making them ideal for all work environments.
4.12 Main Applications of Polypropylene Synthetic Fibers Reinforced Concrete:
- Industrial Floors:Polypropylene Synthetic Fibers significantly enhance tensile strength and toughness, improving flexural strength when combined with rebar.
- Prefabricated Concrete Components:Their antistatic properties make them ideal for ballastless track slabs, while their acid and alkali resistance make them perfect for tunnel segments.
- Fiber-Reinforced Shotcrete:Polypropylene Synthetic Fibers reduce rebound rate and ensure tight adhesion to tunnel walls without cracks.
- High-Performance Concrete:Due to their easy processing and stable, cost-effective performance, polypropylene fibers are widely recognized in UHPC (Ultra-High-Performance Concrete) manufacturing.
4.2 Other Synthetic Fibers:
Besides polypropylene, other fibers such as acrylic, polyester, glass, basalt, nylon, polyoxymethylene, and polyvinyl alcohol fibers also exist. Although their material properties are often superior, they have limitations. For instance, acrylic fibers are suited for asphalt, polyester lacks macrofibers, and glass fibers need to be alkali-resistant. Basalt fibers and the like are much more expensive and lack macrofibers, making them less suitable for structural enhancement.
5. Precautions When Using Synthetic Fibers
5.1 Mixing: When adding fibers at the mixing station, ensure longer mixing times and adjust the proportions based on the fiber type.
5.2 Professional Application: Different application scenarios require different equipment and skilled workers; always employ professional construction teams.
5.3 Maintenance: Adhere strictly to construction and maintenance requirements, even with added synthetic fibers.
I hope this article helps you understand synthetic fiber reinforced concrete better. I’m Director Wang, from a synthetic fiber manufacturing company specializing in high-strength polypropylene fibers.




